Syntax: |
PGPENCRYPT |
[ src file ] [ target file ] [ keyring ] [ options ] |
Arguments: |
[ src file ] |
A variable or string defining the file name of the file to encrypt with PGP. Wildcard characters are not permitted in [ src file ] or [ target file ]. |
|
[ target file ] |
A variable or string defining the file name of the newly encrypted file; if the file existed, it will be overwritten. |
|
[ keyring ] |
Optional variable or string defining the location of an alternate GPG style keyring to be used in the encryption. This option is deprecated and may be removed. |
Options: |
/armor |
Select this option to ASCII armor the [ target file ]. |
|
/comment=xx |
The comment found in the 'Key Name' field for the PGP key of the recipient of the encrypted file; this option may not be necessary if enough information is provided via the /email and/or /user options to uniquely identify the recipient’s public key on your keyring. The comment specified must completely match the comment for the key. |
|
/compat |
Creates an output file compatible with older implementations of PGP but cannot create a file over 2GB in size. |
|
/email=xx |
The e-mail address found in the 'Key Name' field for the PGP key of the recipient of the encrypted file; this option may not be necessary if enough information is provided via the /comment and/or /user options to uniquely identify the recipient’s public key on your keyring. The e-mail address specified must completely match the e-mail address for the key |
|
/pw=xx |
The passphrase associated with the private key you wish to use to digitally sign the file. When using the /sign option; if a passphrase was not saved in the Configurator, this option is required. |
|
/sign |
Select this option if you wish to digitally sign the file using your own private key. If the passphrase for your key was not saved, you will need to additionally use the /pw=xx option to specify the key passphrase. |
|
/signcomment=xx |
The comment found in the 'Key Name' field for signer's private key; this option may not be necessary if enough information is provided via the /signemail and/or /signuser options to uniquely identify the signer's private key on your keyring. The comment specified must completely match the comment for the key. |
|
/signemail=xx |
The e-mail address found in the 'Key Name' field for the signer's private key; this option may not be necessary if enough information is provided via the /signcomment and/or /signuser options to uniquely identify the signer's private key on your keyring. The e-mail address specified must completely match the e-mail address for the key. |
|
/signuser=xx |
The user name found in the 'Key Name' field for the signer's private key; this option may not be necessary if enough information is provided via the /comment and/or /email options to uniquely identify the recipient’s public key on your public keyring. The user name may be a full or partial match of the actual user name if /user option is used without /comment and /email. It must be a complete match if either or both of the /comment or /email options are used. |
|
/textmode |
Select this option if you wish to have [ target file ] saved in a text mode format. |
|
/user=xx |
The user name found in the 'Key Name' field for the PGP key of the signer's private key; this option may not be necessary if enough information is provided via the /signcomment and/or /signemail options to uniquely identify the signer's private key on your keyring. The user name may be a full or partial match of the actual user name if /signuser option is used without /signcomment and /signemail. It must be a complete match if either or both of the /signcomment or /signemail options are used. |
.
This script command encrypts a file using PGP encryption. Files may be decrypted using the Robo-FTP PGPDECRYPT script command or any other PGP or GPG encryption application.
To encrypt a file, you must have an existing keyring containing the private key you wish to use. (If you have multiple private keys on a given keyring, Robo-FTP will always use the first key.) You must also have the public key of the recipient of the file on the keyring and use the /user, /comment, and/or /email options to specify all or part of the key ID for it to be identified. In the Configurator under Manage Keys, you will find the 'Key Name' field. Here you will find the user name, key comment, and an e-mail address, if applicable, associated with a specific key. For example:
Robo-FTP (Support Key) <[email protected]>
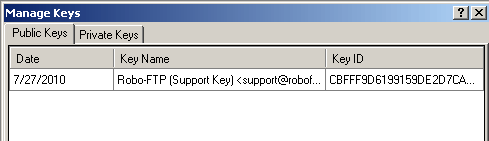
In the above example, Robo-FTP is the user name, Support Key is the key comment, and [email protected] is the e-mail address for the key.
Use the /armor option if you wish the resulting file to be in ASCII armored format.
Use the /sign option if you wish the resulting file to be digitally signed.
Use the /textmode option if you wish the resulting file to be a text mode format.
When signing an encrypted file, you must specify your passphrase either within the command itself using the /pw option or by previously specifying it in the Robo-FTP Configurator.
Important
Robo-FTP secures your passphrase by saving it in an encrypted format in the Windows registry along with its other settings. The passphrase is also never displayed in the Robo-FTP console window nor written to any log file. But be aware that it does appear in clear-text in a script file. Therefore, the method of specifying your passphrase during configuration is the most secure.
It is typical for encrypted files to have an extension of .pgp, .gpg, or .asc (if ascii armored). In most of the examples below, we add one of these extensions at the end of the original file to create the name of the encrypted version of the file. We recommend that you adopt these conventions as well.
Original File Name: "datafile.txt"
Encrypted File Name: "datafile.txt.pgp"
For ASCII armored files (see below):
Original File Name: "datafile.txt"
Encrypted File Name: "datafile.txt.asc"
In the example below a file is encrypted using a public key on the default keyring that is identified by a user name of “Dick Tracy”.
PGPENCRYPT "datafile.txt" "datafile.txt.pgp" /user="Richard Tracy"
In the example below, more of the key ID is specified.
PGPENCRYPT "datafile.txt" "datafile.txt.pgp" /user="Richard Tracy" /[email protected]
The following example encrypts a file and specifies the keyring is in an alternate location.
PGPENCRYPT "datafile.txt" "datafile.txt.pgp" "c:\gnupg" /user="Richard Tracy"
The following example encrypts a file and specifies the output format to be ASCII armored. (The .asc extension is typically used for these types of files.)
PGPENCRYPT "datafile.txt" "datafile.txt.asc /user="Richard Tracy" /armor
The following example encrypts a file for Richard Tracy and digitally signs it using a specified private key (John Doe).
PGPENCRYPT "datafile.txt" "datafile.txt.pgp" /user="Richard" /signuser="John Doe" /pw="John Doe's passphrase"
Important
When encrypting a file, PGP requires the public key of the recipient so that it may only be decrypted with the recipient's private key. The recipient’s public key must be present on your keyring at the time of encryption. Keys are imported to your keyring by way of the PGPIMPORT script command or by using the Import Key functionality in the Robo-FTP Configurator.
Related Command(s): PGPDECRYPT, PGPIMPORT
See also: Robo-FTP and PGP Cryptography, Configure PGP Menu